

The frontal lobe, occipital lobe, parietal lobe, and temporal lobe have different locations and functions that support the responses and actions of the human body. The brain is divided into four sections, known as lobes (as shown in the image). Here we will take a closer look at the four lobes of the brain to discover more about the location and function of each lobe. Composed of 50 to 100 billion neurons, the human brain remains one of the world's greatest unsolved mysteries. The term is ambiguous, with some authors including the paraterminal gyrus, the subcallosal area, the cingulate gyrus, the parahippocampal gyrus, the dentate gyrus, the hippocampus and the subiculum while the Terminologia Anatomica includes the cingulate sulcus, the cingulate gyrus, the isthmus of cingulate gyrus, the fasciolar gyrus, the parahippocampal gyrus, the parahippocampal sulcus, the dentate gyrus, the fimbrodentate sulcus, the fimbria of hippocampus, the collateral sulcus, and the rhinal sulcus, and omits the hippocampus.The human brain is the most complex organ in the body. The limbic lobe is an arc-shaped region of cortex on the medial surface of each cerebral hemisphere of the mammalian brain, consisting of parts of the frontal, parietal and temporal lobes. The temporal lobe is involved in processing sensory input into derived meanings for the appropriate retention of visual memories, language comprehension, and emotion association. The temporal lobe is located beneath the lateral fissure on both cerebral hemispheres of the mammalian brain. There are many extrastriate regions, and these are specialized for different visual tasks, such as visuospatial processing, color differentiation, and motion perception. Visually driven regions outside V1 are called extrastriate cortex. V1 is often also called striate cortex because it can be identified by a large stripe of myelin, the Stria of Gennari.
HOW MANY LOBES ARE IN THE BRAIN 8 FULL
Human V1 is located on the medial side of the occipital lobe within the calcarine sulcus the full extent of V1 often continues onto the posterior pole of the occipital lobe. The primary visual cortex is Brodmann area 17, commonly called V1 (visual one).

The occipital lobe is the visual processing center of the mammalian brain containing most of the anatomical region of the visual cortex. A lesion commonly in the right superior or inferior parietal lobule leads to hemineglect. The superior parietal lobule and inferior parietal lobule are the primary areas of body or spatial awareness. The somatosensory cortex can be illustrated as a distorted figure - the homunculus (Latin: "little man"), in which the body parts are rendered according to how much of the somatosensory cortex is devoted to them. Several areas of the parietal lobe are important in language processing.
HOW MANY LOBES ARE IN THE BRAIN 8 SKIN
The major sensory inputs from the skin (touch, temperature, and pain receptors), relay through the thalamus to the parietal lobe. The parietal lobe integrates sensory information among various modalities, including spatial sense and navigation (proprioception), the main sensory receptive area for the sense of touch (mechanoreception) in the somatosensory cortex which is just posterior to the central sulcus in the postcentral gyrus, and the dorsal stream of the visual system. The parietal lobe is positioned above the occipital lobe and behind the frontal lobe and central sulcus. A report from the National Institute of Mental Health says a gene variant that reduces dopamine activity in the prefrontal cortex is related to poorer performance and inefficient functioning of that brain region during working memory tasks, and to a slightly increased risk for schizophrenia. Dopamine tends to limit and select sensory information arriving from the thalamus to the forebrain.
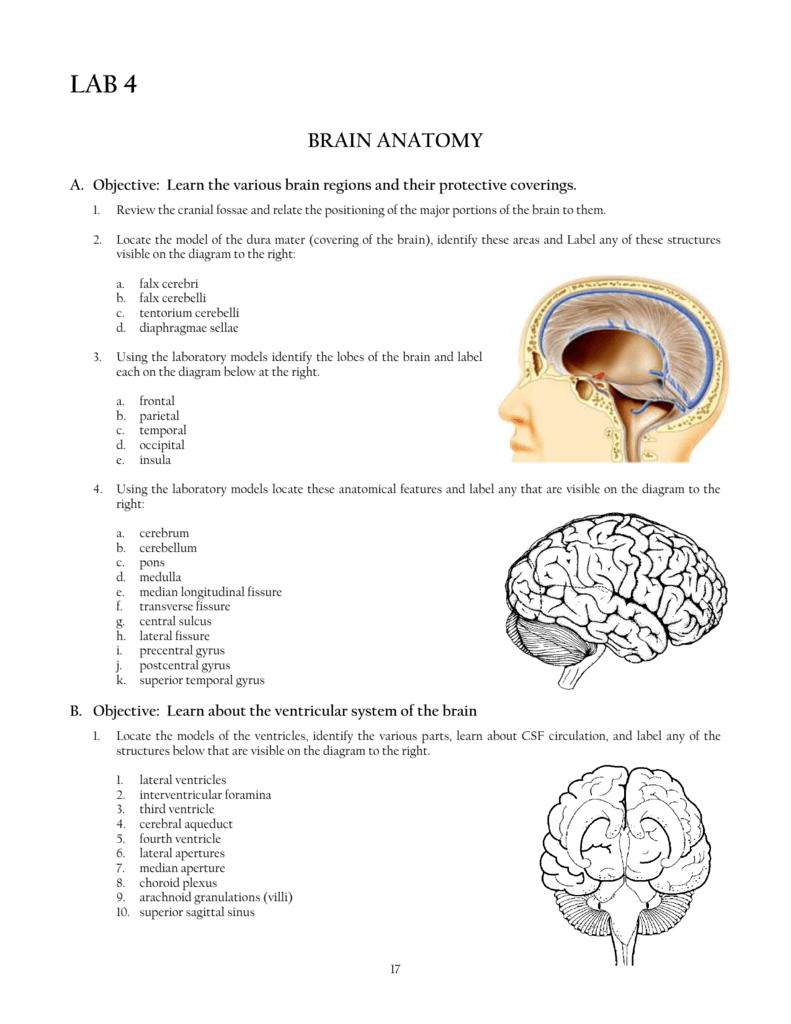
The dopamine system is associated with reward, attention, short-term memory tasks, planning, and motivation. The frontal lobe contains most of the dopamine-delicate neurons in the cerebral cortex. The precentral gyrus, forming the posterior border of the frontal lobe, contains the primary motor cortex, which controls voluntary movements of specific body parts. It is separated from parietal lobe by a space between tissues called the central sulcus, and from the temporal lobe by a deep fold called the lateral sulcus also called the Sylvian fissure. The frontal lobe is located at the front of each cerebral hemisphere and positioned in front of the parietal lobe and above and in front of the temporal lobe. If not specified, the expression "lobes of the brain" refers to the cerebrum. The cerebrum, the largest portion of the human brain, is divided into lobes, but so is the cerebellum. The lobes of the brain were originally a purely anatomical classification, but have been shown also to be related to different brain functions.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
